POLYMER OPTICAL TESTING
HAZE AND LIGHT TRANSMISSION (ASTM D1003)
The molecular structure or degree of crystallinity of a polymer as well as impurities within it affect the scattering of light within that polymer so causing haze. Understandably, haze is only relevant for transparent or translucent materials.
The haze test measures absorption, transmittance and deviation of a direct beam of light by a translucent material. A specimen is placed in the path of a direct beam of bright light. Two properties can be determined:
- Transmittance – The percentage of incident light that is able to pass through the specimen material. The higher the value, the more transparent the material
- Haze – The amount of light that deviates by more than 2.5 Deg from the direction of the incident beam. Materials with haze values greater than 30% are classified as diffusing.
Procedure A uses a Hazemeter and Procedure B a Spectrophotometer. When Hazemeter and Spectrophotometer values differ, the Hazemeter value is taken.
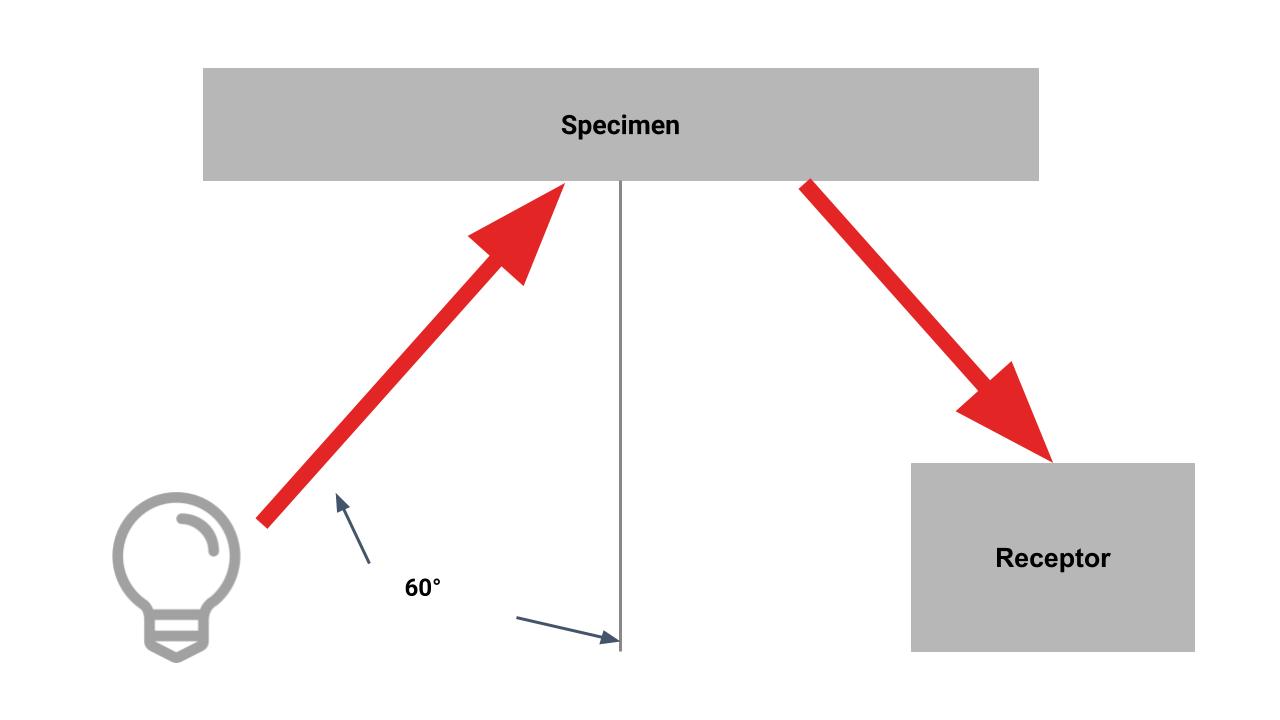

GLOSS (ASTM D253)
Gloss is a measure of the ability of a material to reflect light. A bright light is aimed at the specimen at a specified angle and the brightness of the reflected beam is measured by a photodetector or glossmeter. Polished black glass is used as a standard and is given the value of 100.
The angles used for testing are as follows:
- 20 Deg – For shinier materials. Typically with gloss values higher than 70 at 60 Deg
- 60 Deg – The usual angle for comparing specimens
- 85 Deg – For matt materials. Typically with gloss values lower than 10 at 60 Deg. Commonly known as sheen
It should be stressed that mould design and processing conditions will have an effect on the gloss of a moulded part.